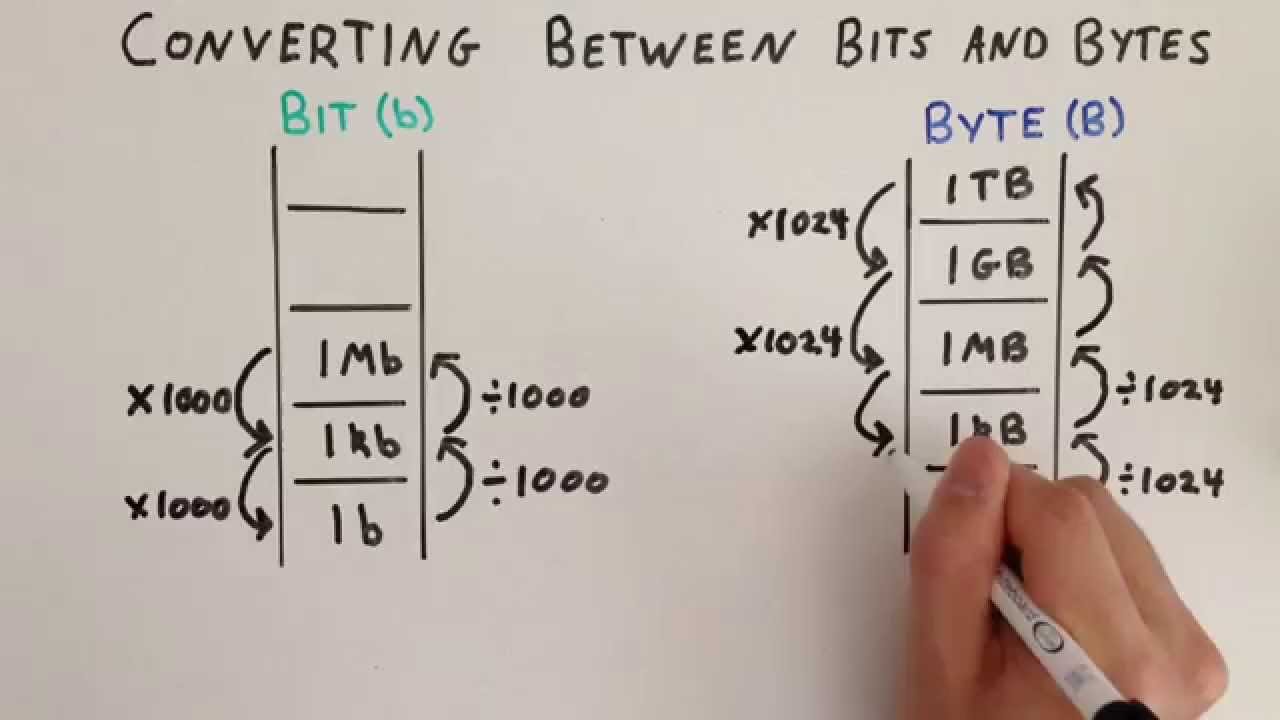
When it comes to computer storage, there are many different units of measurement that can be used to describe the amount of space that is available. Two of the most common units are kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB). A kilobyte is equal to 1,024 bytes, while a megabyte is equal to 1,048,576 bytes. Therefore, 1 MB is equal to 1024 KB. In other words, MB is larger than KB.
The difference between KB and MB is significant, especially when dealing with large files. For example, a 1 GB file would be equal to 1024 MB or 1,048,576 KB. This difference can be important when trying to determine how much space is available on a storage device or how long it will take to transfer a file.
Here are some additional points to remember about KB and MB:
Read also:Brendan Mcloughlin Age A Comprehensive Insight Into His Life And Journey
- KB is a smaller unit of measurement than MB.
- 1 MB is equal to 1024 KB.
- The difference between KB and MB is significant when dealing with large files.
What's Larger
When discussing computer storage, it's crucial to understand the difference between kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB). Here are seven key aspects to consider:
- Size: 1 MB is larger than 1 KB.
- Conversion: 1 MB equals 1024 KB.
- Bytes: 1 KB equals 1024 bytes, while 1 MB equals 1,048,576 bytes.
- Hierarchy: MB is a larger unit of measurement than KB.
- Capacity: MB is used to measure larger storage capacities, while KB is used for smaller ones.
- Data Transfer: Transferring MB takes longer than KB due to the larger file size.
- Storage Devices: Hard drives and SSDs are measured in MB or GB (gigabytes), while RAM is measured in KB or MB.
Comprehending these aspects is essential for effectively managing and understanding computer storage. For instance, when downloading a large file, knowing that MB represents a larger size than KB helps estimate the download time accurately. Additionally, when comparing storage devices, the capacity in MB or GB provides a clear indication of their storage capabilities.
1. Size
Understanding this statement is crucial when exploring the relationship between kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB) in the context of "what's larger kb or mb." It establishes the fundamental comparison between these units, providing a basis for further exploration.
- Storage Capacity:
In terms of storage capacity, 1 MB represents a larger space than 1 KB. This is because MB is a larger unit of measurement, accommodating more data. This distinction becomes significant when dealing with large files or storage devices with substantial capacities.
- File Size Comparison:
When comparing file sizes, a file measured in MB will be larger than a file measured in KB. This is because MB represents a greater quantity of data, indicating that the file contains more information or content.
- Data Transfer:
In the context of data transfer, transferring a file measured in MB will take longer than transferring a file measured in KB. This is because MB represents a larger amount of data that needs to be transmitted, resulting in a longer transfer time.
Read also:
- Alice Braga Who Stole Her Heart
Comprehending this fundamental relationship between MB and KB is essential for effectively managing and understanding computer storage. It provides a foundation for further discussions on data storage, file sizes, and data transfer rates.
2. Conversion
This conversion rate is crucial for understanding the relationship between kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB) in the context of "what's larger kb or mb." It establishes a precise numerical connection between these units, providing a foundation for further exploration.
- Unit Equivalence:
This conversion rate defines the equivalence between MB and KB, making it easier to compare and convert values between these units. For instance, knowing that 1 MB equals 1024 KB allows us to quickly determine that a file size of 2 MB is equivalent to 2048 KB.
- Data Storage and Transfer:
In the context of data storage and transfer, this conversion rate becomes significant. When dealing with large data sets or storage devices with high capacities, it helps us accurately calculate the amount of data involved. For example, a hard drive with a capacity of 500 GB can store approximately 524,288 MB of data, which is equivalent to 536,870,912 KB.
- File Size Comparison:
This conversion rate also enables us to compare file sizes effectively. By converting the file sizes to a common unit, such as MB, we can easily determine which file is larger. For instance, if we have two files, one with a size of 1.5 MB and the other with a size of 1536 KB, we can conclude that both files have the same size.
- Data Transmission Rates:
In the context of data transmission rates, understanding this conversion rate is essential. When dealing with high-speed data transfers, such as those involving fiber optic cables or broadband internet connections, the conversion rate between MB and KB helps us calculate the approximate time required to transfer a given amount of data.
In summary, the conversion rate of 1 MB equals 1024 KB provides a fundamental understanding of the relationship between these units. It enables us to compare and convert values, calculate data storage capacities, compare file sizes, and estimate data transmission rates accurately.
3. Bytes
Understanding the relationship between bytes, kilobytes (KB), and megabytes (MB) is fundamental to comprehending "what's larger kb or mb." This connection establishes the foundation for measuring and comparing data storage capacities and file sizes in computing systems.
- Unit Equivalence:
This relationship defines the equivalence between bytes, KB, and MB. It provides a clear understanding of how these units are related and enables us to convert values between them accurately. For instance, knowing that 1 KB equals 1024 bytes allows us to calculate that a file size of 5 KB is equivalent to 5120 bytes.
- Data Storage and Transfer:
In the context of data storage and transfer, this relationship becomes crucial. When dealing with large data sets or storage devices with high capacities, it helps us precisely calculate the amount of data involved. For example, a hard drive with a capacity of 1 TB (terabyte) can store approximately 1,099,511,627,776 bytes, which is equivalent to 1,073,741,824 KB or 1,024 GB (gigabytes).
- File Size Comparison:
This relationship also enables us to compare file sizes effectively. By converting the file sizes to a common unit, such as bytes, we can easily determine which file is larger. For instance, if we have two files, one with a size of 2.5 MB and the other with a size of 2,621,440 bytes, we can conclude that both files have the same size.
- Data Transmission Rates:
In the context of data transmission rates, understanding this relationship is essential. When dealing with high-speed data transfers, such as those involving fiber optic cables or broadband internet connections, the conversion rates between bytes, KB, and MB help us calculate the approximate time required to transfer a given amount of data.
In summary, the relationship between bytes, KB, and MB provides a fundamental understanding of data measurement and comparison. It enables us to convert values, calculate data storage capacities, compare file sizes, and estimate data transmission rates accurately, which is critical for effectively managing and understanding computer storage.
4. Hierarchy
The hierarchical relationship between megabytes (MB) and kilobytes (KB) is fundamental to understanding "what's larger kb or mb." This hierarchy establishes a clear order and magnitude difference between these units, providing a basis for comparing and measuring data storage capacities and file sizes.
- Unit Classification:
In the hierarchy of data measurement units, MB belongs to a larger unit classification than KB. This means that 1 MB represents a greater quantity of data than 1 KB. This classification is essential for organizing and managing data storage systems, ensuring that data is stored and accessed efficiently.
- Data Storage Capacity:
When comparing data storage capacities, MB is used to measure larger amounts of data than KB. For instance, a hard drive with a capacity of 500 MB can store more data than a hard drive with a capacity of 500 KB. Understanding this hierarchy helps determine the appropriate storage device for specific data storage needs.
- File Size Measurement:
In the context of file sizes, MB is used to measure larger files than KB. For example, a video file with a size of 10 MB is larger than a text file with a size of 10 KB. This hierarchy enables efficient file management and organization, allowing users to quickly identify and access files based on their sizes.
- Data Transfer Rates:
In the context of data transfer rates, understanding the hierarchy between MB and KB is important for estimating transfer times. Transferring a file of 10 MB will take longer than transferring a file of 10 KB over the same network connection. This hierarchy helps network administrators and users plan and optimize data transfer processes.
In summary, the hierarchical relationship between MB and KB provides a structured and logical framework for measuring and comparing data storage capacities and file sizes. This hierarchy is essential for effectively managing and understanding computer storage systems.
5. Capacity
The relationship between storage capacity and the units of measurement, megabytes (MB), and kilobytes (KB), is a fundamental aspect of understanding "what's larger kb or mb." This connection becomes particularly important when dealing with large amounts of data and storage devices with varying capacities.
MB is used to measure larger storage capacities because it represents a greater quantity of data than KB. This distinction is significant when considering the storage capacity of devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and USB flash drives. For instance, a hard drive with a capacity of 500 GB (gigabytes) can store significantly more data than a USB flash drive with a capacity of 16 GB. Understanding this relationship helps determine the appropriate storage device for specific data storage needs.
Conversely, KB is used to measure smaller storage capacities, typically for smaller files and data sets. For example, a text file containing a few hundred words may have a size of a few KB, while a high-resolution image file could have a size of several MB. This distinction is important for managing and organizing files efficiently, as it allows users to quickly identify and access files based on their sizes.
In summary, the connection between storage capacity and the units of measurement, MB and KB, is crucial for understanding "what's larger kb or mb." This relationship helps determine the appropriate storage device for specific data storage needs and enables efficient file management and organization.
6. Data Transfer
The relationship between data transfer rates and the units of measurement, megabytes (MB) and kilobytes (KB), is a crucial aspect of understanding "what's larger kb or mb." This connection becomes particularly important when dealing with large files and high-speed data transfer technologies.
- File Size and Transfer Time:
The size of a file directly influences the time it takes to transfer. A file with a larger size, measured in MB, will take longer to transfer than a file with a smaller size, measured in KB, over the same network connection. This is because a larger file contains more data that needs to be transmitted, resulting in a longer transfer time.
- Network Bandwidth and Transfer Rate:
The bandwidth of a network connection also plays a significant role in data transfer rates. A network with a higher bandwidth can transfer data faster than a network with a lower bandwidth. This means that even if two files have the same size, the file being transferred over a network with a higher bandwidth will transfer faster. Understanding the relationship between file size, network bandwidth, and transfer rate is essential for optimizing data transfer processes.
- Data Compression and Transfer Efficiency:
Data compression techniques can be used to reduce the size of a file before transferring it. This can significantly improve transfer times, especially for large files. Compressed files are smaller in size, which means they take less time to transfer over a network. However, the compression and decompression process itself can add some overhead, so it's important to consider the trade-offs involved.
- Storage Device Performance:
The performance of the storage devices involved in the data transfer process can also affect the transfer rate. Faster storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), can transfer data more quickly than slower storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs). This is because SSDs have faster read and write speeds, which can reduce the overall transfer time.
In summary, the connection between data transfer rates and the units of measurement, MB and KB, is crucial for understanding "what's larger kb or mb." This relationship, along with factors such as network bandwidth, data compression, and storage device performance, plays a significant role in determining the time it takes to transfer files.
7. Storage Devices
The connection between storage devices and the units of measurement, megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and kilobytes (KB), is crucial for understanding "what's larger kb or mb." This relationship becomes particularly important when comparing the storage capacities of different types of storage devices, such as hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and random access memory (RAM).
Hard drives and SSDs are used to store large amounts of data, such as operating systems, applications, and personal files. These devices are measured in MB or GB because they can store significantly more data than RAM. For instance, a hard drive with a capacity of 1 TB (terabyte) can store approximately 1,000 GB of data, while a USB flash drive with a capacity of 16 GB can store approximately 16,000 MB of data. Understanding this relationship helps determine the appropriate storage device for specific data storage needs.
On the other hand, RAM is used to store temporary data that is being actively processed by the computer's central processing unit (CPU). RAM is measured in KB or MB because it typically stores smaller amounts of data than hard drives or SSDs. For example, a computer with 8 GB of RAM can store approximately 8,000 MB of data. This data is used to store the operating system, running applications, and recently accessed files. Understanding this relationship helps optimize computer performance by ensuring that there is sufficient RAM to handle the current workload.
In summary, the connection between storage devices and the units of measurement, MB, GB, and KB, is essential for understanding "what's larger kb or mb." This relationship helps determine the appropriate storage device for specific data storage needs and ensures that there is sufficient RAM to handle the current workload.
Frequently Asked Questions about "What's Larger
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions regarding the comparison between kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB), providing clear and informative answers.
Question 1: Which is larger, a kilobyte or a megabyte?
A megabyte (MB) is larger than a kilobyte (KB). 1 MB is equal to 1,024 KB.
Question 2: How many bytes are in a kilobyte?
1 kilobyte (KB) is equal to 1,024 bytes.
Question 3: How many kilobytes are in a megabyte?
1 megabyte (MB) is equal to 1,024 kilobytes (KB).
Question 4: Which unit of measurement is used for larger storage capacities, such as hard drives and SSDs?
Megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB) are commonly used to measure larger storage capacities.
Question 5: Which unit of measurement is used for smaller amounts of data, such as RAM?
Kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB) are commonly used to measure smaller amounts of data, such as RAM.
Question 6: Why is it important to understand the difference between KB and MB?
Understanding the difference between KB and MB is important for accurately measuring and comparing data storage capacities and file sizes. It also helps in estimating data transfer times and choosing the appropriate storage devices for specific needs.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between KB and MB, enabling readers to confidently navigate and manage their digital storage needs.
Transition to the next article section...
Tips for Understanding "What's Larger
To enhance your comprehension of the relationship between kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB), consider these valuable tips:
Tip 1: Remember the Conversion Rate
Always keep in mind that 1 MB is equal to 1,024 KB. This fundamental conversion rate serves as the cornerstone for all calculations and comparisons involving KB and MB.
Tip 2: Understand the Hierarchy
Recognize that MB represents a larger unit of measurement than KB. This hierarchical relationship forms the basis for comparing and measuring data storage capacities and file sizes.
Tip 3: Consider Storage Capacity
When dealing with larger storage capacities, such as those of hard drives and SSDs, MB and GB (gigabytes) are commonly used. This is because these units can accommodate more significant amounts of data.
Tip 4: Measure Smaller Data Amounts with KB
For measuring smaller data amounts, such as the size of RAM or individual files, KB and MB are typically employed. These units provide a more precise measurement for smaller data sets.
Tip 5: Estimate Data Transfer Times
Comprehending the relationship between KB and MB is crucial for estimating data transfer times. Larger file sizes (measured in MB) will take longer to transfer compared to smaller file sizes (measured in KB), assuming the same network conditions.
Tip 6: Choose the Right Storage Device
Understanding the difference between KB and MB is essential when selecting the appropriate storage device for your needs. Consider the capacity and intended usage to determine whether MB or GB is the more suitable unit of measurement.
Tip 7: Optimize File Management
By understanding the relationship between KB and MB, you can optimize your file management practices. This includes efficiently organizing and storing files based on their sizes, ensuring optimal storage utilization.
Tip 8: Enhance Data Transfer Efficiency
Optimizing data transfer efficiency requires an understanding of KB and MB. Compressing files before transferring can reduce their size (measured in KB or MB), thereby improving transfer speeds.
By following these tips, you can effectively grasp the concept of "what's larger: KB or MB?" and confidently navigate the world of data storage and transfer.
Transition to the article's conclusion...
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the concept of "what's larger kb or mb," delving into the fundamental relationship between kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB). We established that MB is larger than KB, with a conversion rate of 1 MB being equal to 1,024 KB. This understanding forms the basis for comparing and measuring data storage capacities and file sizes.
We emphasized the importance of considering storage capacity when choosing the appropriate unit of measurement. For larger storage capacities, such as those of hard drives and SSDs, MB and GB (gigabytes) are commonly used. Conversely, KB and MB are typically employed for measuring smaller data amounts, such as the size of RAM or individual files.
Furthermore, we highlighted the significance of understanding KB and MB in optimizing data transfer times and file management practices. By comprehending the relationship between these units, you can make informed decisions about data storage and transfer, ensuring efficiency and optimal utilization.
In conclusion, grasping the concept of "what's larger kb or mb" empowers you to navigate the world of data storage and transfer with confidence. Whether you are managing files, selecting storage devices, or estimating transfer times, this understanding serves as a valuable tool for effective data management and utilization.
![Which Is Bigger MB or KB? [2024 Guide] PC Strike](https://i2.wp.com/pcstrike.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Which-Is-Bigger-MB-or-KB.png)
![Is KB bigger than MB? [The Complete Guide] Technize](https://i2.wp.com/technize.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/Which-is-bigger-KB-or-MB.jpg)