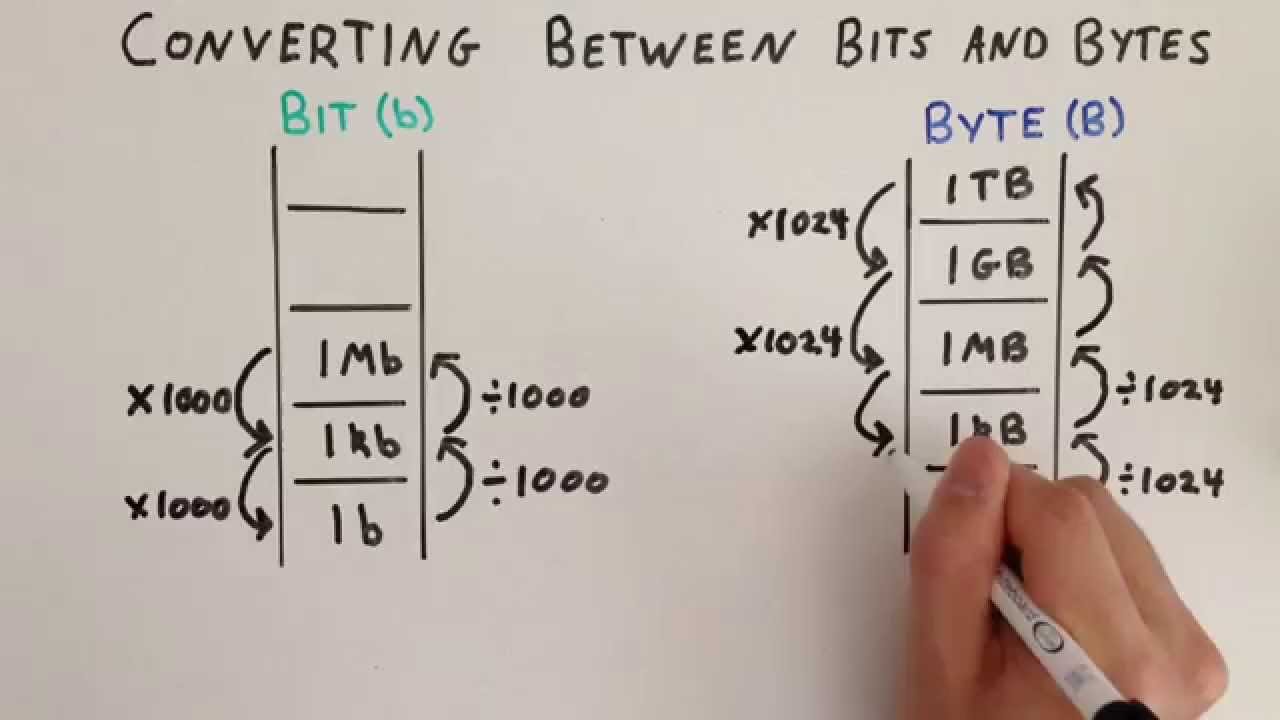
KB, MB, GB, and TB are all units of digital storage capacity. The term "KB" stands for kilobyte, "MB" stands for megabyte, "GB" stands for gigabyte, and "TB" stands for terabyte.
These units are used to measure the amount of data that can be stored on a computer or other electronic device. The most common unit of measurement for digital storage is the gigabyte. A gigabyte is equal to 1,024 megabytes, or 1,048,576 kilobytes. A terabyte is equal to 1,024 gigabytes, or 1,073,741,824 kilobytes.
The size of a digital file is typically measured in kilobytes, megabytes, or gigabytes. For example, a text file might be a few kilobytes in size, while a music file might be a few megabytes in size, and a video file might be a few gigabytes in size.
Read also:Meet The Extraordinary Damian Musk Making Waves In Business And Innovation
Units of Digital Storage
Understanding the different units of digital storage is essential for managing and storing data effectively. Here are seven key aspects to consider:
- Bytes
- Kilobytes (KB)
- Megabytes (MB)
- Gigabytes (GB)
- Terabytes (TB)
- Storage Capacity
- Data Measurement
These aspects are interconnected and provide a comprehensive understanding of digital storage. Bytes are the temel building blocks of digital data, and multiples of bytes are used to represent larger units such as KB, MB, and GB. The capacity of storage devices, such as hard drives and USB drives, is typically measured in GB or TB. Understanding these units is also crucial for data measurement, as file sizes and storage space are commonly expressed in MB or GB.
1. Bytes
Bytes are the fundamental units of digital information. They represent individual characters, numbers, or symbols in a computer system. In the context of "KB, MB, GB, TB," bytes are the building blocks for larger units of storage capacity.
- Size and Value: A single byte consists of 8 bits and can represent 256 different values, ranging from 0 to 255. This allows bytes to encode various types of data, including text, numbers, and binary code.
- Data Representation: Bytes are used to represent data in computers and digital devices. For example, a text file is a collection of bytes, each representing a character. Similarly, an image file is made up of bytes that define the color and position of each pixel.
- Storage Capacity: While bytes are the smallest unit of storage, they are often combined to form larger units such as kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB). These larger units are more practical for measuring the storage capacity of devices and files.
- Data Transmission: Bytes are also used to transmit data over networks. For example, when you download a file from the internet, the data is broken down into bytes and transmitted over the network. Once received, the bytes are reassembled to form the original file.
In summary, bytes are the foundational elements of digital storage and data representation. They are combined to create larger units of storage capacity and are essential for the transmission and storage of information in computer systems and devices.
2. Kilobytes (KB)
Kilobytes (KB) are a unit of digital storage capacity equal to 1,024 bytes. In the context of "kb kb mb mb," KB represents a small amount of storage capacity, often used to measure the size of text files, small images, or basic software programs.
- Data Measurement: KB is commonly used to measure the size of small digital files. For example, a text document containing a few hundred words might be a few KB in size. This makes KB a suitable unit for measuring the size of individual files or small collections of data.
- Storage Capacity: While KB is not a large unit of storage capacity by today's standards, it was a significant unit in the early days of computing. Floppy disks, a common storage medium in the 1980s and 1990s, had a storage capacity of a few hundred KB.
- Comparison to Other Units: KB is smaller than other commonly used storage units such as megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB). 1 MB is equal to 1024 KB, and 1 GB is equal to 1024 MB. This hierarchy of storage units helps us understand the relative sizes of different files and storage devices.
- Historical Significance: KB played a significant role in the development of computing. As storage capacities increased, the term "KB" became less commonly used for measuring large amounts of data. However, it remains a useful unit for measuring small files or understanding the historical context of data storage.
In summary, kilobytes (KB) are a unit of digital storage capacity that represents a small amount of data. They are commonly used to measure the size of individual files or small collections of data. While KB is not a large unit of storage capacity by today's standards, it played a significant role in the early days of computing and remains a useful unit for certain purposes.
Read also:Exploring The Magic Of Saratoga Springs Disney A Comprehensive Guide
3. Megabytes (MB)
Megabytes (MB) are a unit of digital storage capacity equal to 1,024 kilobytes (KB). In the context of "kb kb mb mb," MB represents a larger amount of storage capacity than KB, commonly used to measure the size of larger files, such as images, music files, and software applications.
The connection between MB and "kb kb mb mb" is hierarchical. KB is a smaller unit of storage capacity than MB, and MB is a smaller unit than GB (gigabytes) and TB (terabytes). This hierarchy allows us to express different storage capacities in a structured and comparative way.
For example, a digital photo might be a few MB in size, while a music file might be tens of MB in size. Similarly, a software application might be hundreds of MB in size. Understanding the relationship between MB and other storage units is essential for managing and organizing digital data effectively.
In practical terms, MB is a commonly used unit for measuring the size of files and storage devices. USB flash drives, for instance, often have capacities ranging from a few hundred MB to several gigabytes. Hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) used in computers typically have capacities of hundreds of gigabytes or even terabytes.
Overall, megabytes (MB) are an important unit of digital storage capacity, larger than kilobytes (KB) but smaller than gigabytes (GB) and terabytes (TB). Understanding the relationship between MB and other storage units is crucial for effectively managing and storing digital data.
4. Gigabytes (GB)
Gigabytes (GB) are a unit of digital storage capacity equal to 1,024 megabytes (MB) or 1,073,741,824 bytes. In the context of "kb kb mb mb," GB represents a larger amount of storage capacity than MB, commonly used to measure the size of large files, such as high-quality images, videos, and software applications.
- Data Storage: GB is commonly used to measure the storage capacity of hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) used in computers. HDDs and SSDs with capacities ranging from hundreds of GB to several TB are widely available.
- File Size Measurement: GB is also used to measure the size of large files, such as video files, game files, and software installers. Understanding the size of files in GB helps in managing storage space and estimating download or upload times.
- Device Capacity: The capacity of USB flash drives and external hard drives is often measured in GB. These devices are commonly used to store and transfer large amounts of data, such as backups, media files, and software.
- Cloud Storage: Many cloud storage services offer plans with different storage capacities measured in GB. Users can choose a plan that meets their storage needs, whether it's for personal files, business documents, or large media libraries.
In summary, gigabytes (GB) are an important unit of digital storage capacity, larger than megabytes (MB) but smaller than terabytes (TB). GB is commonly used to measure the storage capacity of devices, the size of large files, and the capacity of cloud storage plans.
5. Terabytes (TB)
In the hierarchy of digital storage units, terabytes (TB) represent a vast amount of storage capacity, dwarfing kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), and gigabytes (GB). TB is primarily used to measure and manage extremely large datasets and high-resolution media files.
- Data Storage: TB is commonly employed to store large volumes of data in enterprise servers, cloud storage platforms, and high-performance computing systems. These systems handle massive datasets used for scientific research, data analytics, and digital archiving.
- Media Content: TB is essential for storing high-resolution videos, movies, and music libraries. With the advent of 4K and 8K video formats, TB has become the standard unit for storing and distributing large media files.
- Backup and Archiving: TB is ideal for backing up and archiving large amounts of data, ensuring the preservation of critical information. It allows for the storage of multiple backups and long-term retention of data for disaster recovery and compliance purposes.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage providers offer TB-level storage plans for businesses and individuals who require vast amounts of online storage space. These plans enable users to store, access, and share large datasets remotely.
In summary, TB is a crucial unit of digital storage capacity in the era of big data and high-resolution media consumption. It empowers businesses, researchers, and individuals to manage and store vast amounts of data, enabling advancements in various fields and facilitating the preservation of digital information.
6. Storage Capacity
Storage capacity, measured in units such as kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB), is a fundamental aspect of digital devices. It determines the amount of data that can be stored on a particular device, ranging from small text files to vast media libraries and scientific datasets. Understanding storage capacity is crucial for managing and utilizing digital information effectively.
The connection between storage capacity and "kb kb mb mb" lies in the hierarchical nature of these units. KB, MB, GB, and TB represent progressively larger storage capacities, with 1 KB being equal to 1,024 bytes, 1 MB being equal to 1,024 KB, 1 GB being equal to 1,024 MB, and 1 TB being equal to 1,024 GB. This hierarchy allows for precise measurement and comparison of storage capacities across devices and applications.
The practical significance of understanding storage capacity is evident in various scenarios. For instance, when choosing a new computer or smartphone, users need to consider the storage capacity required to meet their needs. Similarly, when storing large files such as videos or software, users need to ensure that their storage device has sufficient capacity to accommodate the files. Additionally, storage capacity plays a vital role in cloud storage services, where users can purchase plans with varying storage limits based on their requirements.
In summary, storage capacity, measured in units such as KB, MB, GB, and TB, is a crucial aspect of digital devices and applications. Understanding the connection between these units and the practical significance of storage capacity empowers users to make informed decisions when managing their digital data and utilizing digital devices effectively.
7. Data Measurement
Data measurement lies at the heart of understanding and managing digital information. In the context of "kb kb mb mb," data measurement refers to the process of quantifying the amount of data stored or transmitted in digital systems.
The connection between data measurement and "kb kb mb mb" is fundamental because these units represent the standard measures used to express digital storage capacity and data size. Kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB) form a hierarchical system, with each unit representing a multiple of the previous one. This allows for precise measurement and comparison of data volumes across different devices, applications, and networks.
Data measurement is crucial for several practical reasons. Firstly, it enables efficient storage management. By understanding the size of data files, users can allocate storage space accordingly, avoiding both wastage and insufficient capacity. Secondly, data measurement is essential for data transmission. Networks and protocols rely on accurate measurement to ensure that data packets are transmitted and received correctly, without errors or loss of information.
Furthermore, data measurement plays a vital role in data analysis and processing. By measuring the size and distribution of data, organizations can gain insights into data patterns, trends, and anomalies. This information can be leveraged for decision-making, optimization, and predictive modeling.
In summary, data measurement, as represented by units like KB, MB, GB, and TB, is a fundamental aspect of digital information management. It enables efficient storage, reliable transmission, and informed data analysis, empowering individuals and organizations to harness the full potential of digital technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions about "kb kb mb mb"
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the units of digital storage capacity, namely kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB).
Question 1: What is the relationship between KB, MB, GB, and TB?
Answer: KB, MB, GB, and TB represent a hierarchical system of digital storage units. Each unit is a multiple of the previous one, with 1 KB being equal to 1,024 bytes, 1 MB being equal to 1,024 KB, and so on.
Question 2: How do I convert between these units?
Answer: To convert from a larger unit to a smaller unit, multiply by 1,024. To convert from a smaller unit to a larger unit, divide by 1,024.
Question 3: What is a good rule of thumb for estimating the size of different types of files?
Answer: As a general guide, text files are typically measured in KB, images in MB, videos in GB, and large software applications in TB.
Question 4: Can I have a fraction of a KB, MB, GB, or TB?
Answer: No, these units are always whole numbers. However, decimal values can be used to represent fractions of a unit, such as 2.5 GB or 0.75 TB.
Question 5: Are there units larger than TB?
Answer: Yes, there are larger units such as petabytes (PB), exabytes (EB), and zettabytes (ZB). However, these units are less commonly used.
Question 6: How can I manage storage space effectively?
Answer: To manage storage space effectively, regularly review your files and delete or archive anything you no longer need. Consider using cloud storage services for large files or infrequently accessed data.
In summary, understanding the relationship between KB, MB, GB, and TB is essential for managing and storing digital data effectively. By familiarizing yourself with these units and their conversions, you can make informed decisions about storage allocation and data management.
Thank you for reading this FAQ section. For further information, please refer to the main article above.
Tips for Understanding and Using "KB, MB, GB, and TB"
To effectively use and manage digital storage, it is essential to understand the concepts and relationships between different units of storage capacity, namely kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB).
Tip 1: Understand the Hierarchy
KB, MB, GB, and TB form a hierarchical system, with each unit being a multiple of the previous one. Specifically, 1 KB equals 1,024 bytes, 1 MB equals 1,024 KB, 1 GB equals 1,024 MB, and 1 TB equals 1,024 GB.
Tip 2: Convert Between Units
To convert from a larger unit to a smaller unit, multiply by 1,024. Conversely, to convert from a smaller unit to a larger unit, divide by 1,024.
Tip 3: Estimate File Sizes
As a general guideline, text files are typically measured in KB, images in MB, videos in GB, and large software applications in TB.
Tip 4: Use Decimal Values
While KB, MB, GB, and TB are always whole numbers, decimal values can be used to represent fractions of a unit. For instance, 2.5 GB or 0.75 TB are valid representations.
Tip 5: Consider Larger Units
Beyond TB, there are larger units of storage capacity such as petabytes (PB), exabytes (EB), and zettabytes (ZB). These units are becoming increasingly relevant as data storage needs continue to grow.
Tip 6: Manage Storage Space Effectively
To manage storage space effectively, regularly review your files and delete or archive anything you no longer need. Additionally, consider using cloud storage services for large files or infrequently accessed data.
By following these tips, you can gain a better understanding of KB, MB, GB, and TB, and effectively manage and utilize digital storage capacity.
In conclusion, understanding the concepts and relationships between different units of storage capacity is crucial for efficient data management and storage optimization.
Conclusion
In summary, "KB, MB, GB, and TB" are fundamental units of digital storage capacity, each representing a specific amount of data. Understanding their relationship and how to use them effectively is crucial for managing and storing digital information.
As the world continues to generate and consume vast amounts of data, the need for efficient storage solutions becomes increasingly important. By leveraging our understanding of these storage units, we can optimize our use of storage devices, cloud services, and other data management systems.